WHAT IS HAZOP?
The hazard and operability (HAZOP) study is a way of identifying potential hazards and problems caused by deviations from the ideal design of the plant.
It is the most widely used aid to loss prevention because:
• It is easy to learn.
• It can be easily adapted to almost all the operations that are carried out within process industries.
• No special level of academic qualification is required.
Hierchy of Plant Safety
THE HAZOP TEAM
The team conducting the HAZOP study should consist of people who have good understanding of the process and plant.
• Chairman
• Scribe
• Process representative
• Control Systems representative
• Operations representative
PROCEDURE
1. Subdivide the P&IDs into smaller nodes. Start at the beginning of the process flow. Provide details of the design intention of the node, including information on flowrates, pressures, and temperatures, etc.
2. Simulate problems that arise as results of deviation from ideal design.
Guide Terms: Parameters:
No/Less/More Flow, Level, Pressure, Temperature
3. Develop the
causes of the deviation in question through brainstorming.
Remember: Cause in the node, consequence everywhere.
4. Evaluate the consequences of each cause. Rate each consequence based on its likelihood and severity. The knowledge base of the team will have a significant effect on their ability to predict the consequences of a particular event.
Likelihood
L1- Extremely Unlikely
Never heard of in the industry but not entirely incredible.
L2 - Very Unlikely
Accident once every 10 years within industry.
L3 - Unlikely
Accident once every 1–5 years within industry
L4 - Probable
More than once a year within industry. Possibility of repeated incidents
Severity
S1 Neglibigle
[S] No injury or first aid
[A] Minimal equipment damage (less than $200K)
[E] Contained within facility. No adverse environmental impact.
S2 Marginal
[S] Lost time injury
[A] Minor equipment damage ($200K - $2M ).Downtime less than one day.
[E] Contained within facility. Minimal impact and no long term threat to environment
S3 Critical
[S] Dingle fatality. Threat to public.
[A] Major equipment damage ($2M - $10M). Downtime of 1 to 10 days.
[E] Offsite releases, with potential for significant adverse impact.
S4 Catastrophic
[S] Multiple fatalities. Fatality harm to public sector.
[A] Extensive equipment damage (greater than $10M). Downtime of more than 10 days.
[E] Major environmental impact. Regulatory reporting required.
5. Identify Safeguards. Discuss safeguards that may either reduce the likelihood of the problem or mitigate the effects of the problem. The safeguards must be directly proportional to the risk.
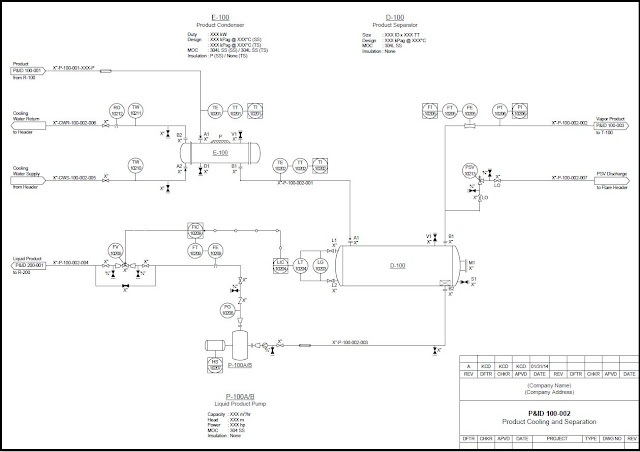
SAMPLE HAZOP STUDY
P&ID BEFORE HAZOP
P&ID AFTER HAZOP